
The satellite geospatial and communication sectors are undergoing rapid transformation, driven by a myriad of factors and forces that are reshaping industry dynamics and technological landscapes, including mergers and acquisitions (M&A) that reshape industry dynamics and capabilities. These sectors, which encompass everything from high-resolution Earth observation to global broadband connectivity, are influenced by a complex interplay of technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, market demands, and strategic initiatives by key industry players.
Technological Advancements
Technological innovation lies at the heart of the satellite industry's evolution. Companies like SpaceX and OneWeb are leading the charge with ambitious projects to deploy large constellations of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites. SpaceX's Starlink aims to provide global broadband internet coverage, leveraging advancements in satellite miniaturization and launch capabilities to reduce costs and increase efficiency. Similarly, OneWeb seeks to bridge the digital divide by offering high-speed internet access to underserved regions through its satellite constellation.
Advances in satellite imaging and data analytics are also transforming the geospatial sector. Maxar Technologies, for example, combines high-resolution imagery from its satellites with sophisticated analytics to support applications ranging from urban planning and agriculture to disaster response and national security. These technological advancements not only enhance operational capabilities but also drive market demand for more reliable and accurate geospatial information.
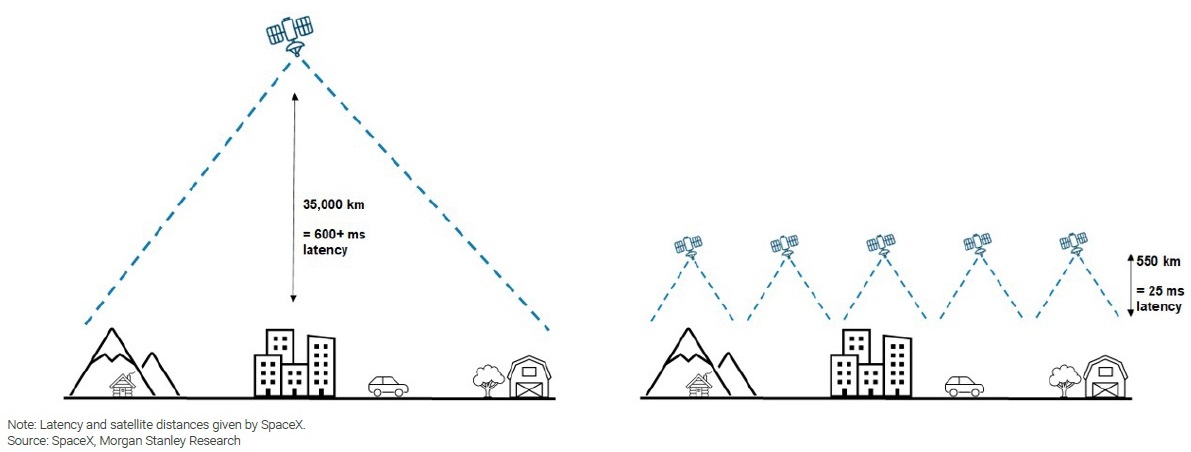
Geostationary Operational Environmental (GOES) vs Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellites
Revenue and Market Impact
Companies such as Maxar Technologies and SES demonstrate significant financial scale and market influence within the satellite sector. Maxar, known for its advanced Earth observation capabilities, reported revenues of approximately $1.6 billion in 2023, driven by its integrated geospatial solutions and satellite imaging services. SES, a major player in satellite communication services, reported revenues of around €1.9 billion ($2.1 billion) in 2023, leveraging its fleet of GEO and MEO satellites to deliver broadcasting, broadband, and government communication services globally.
Research and Development (R&D) and Innovation
Substantial R&D investments drive innovation in satellite technologies. Iridium Communications, for instance, continually enhances its LEO satellite network to deliver reliable global connectivity. Telesat's development of the Lightspeed constellation underscores ongoing efforts to advance broadband capabilities, reflecting a competitive landscape where innovation and operational excellence are paramount.
Industry Growth Rates
The satellite communication industry has seen robust growth over recent years, driven by technological advancements, increasing demand for connectivity, and the expansion of applications across various sectors. The growth rates in this industry are typically measured in terms of market size, revenue, and number of satellites launched.
- Satellite Communication Industry:
- Overall Market: CAGR of 6.2% (2021-2026)
- VSAT Market: CAGR of 8.5% (2021-2028)
- Satellite Broadband: CAGR of 11.0% (2020-2025)
- Number of Satellites Launched: Annual growth rate of approximately 15% (2021-2030)
The geospatial industry has also been experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing use of geospatial data across various sectors, advancements in technology, and the integration of geospatial information with other data sources.
- Geospatial Industry:
- Overall Geospatial Analytics Market: CAGR of 10.9% (2020-2025)
- Geospatial Solutions Market: CAGR of 10.7% (2020-2030)
- Remote Sensing Market: CAGR of 8.6% (2020-2028)
- GIS Market: CAGR of 12.4% (2020-2025)
Both industries are poised for continued growth, driven by technological advancements, increasing demand for data and connectivity, and expanding applications across various sectors.
Mergers and Acquisitions
M&A activity within the satellite sector plays a pivotal role in shaping industry consolidation and technological leadership. Notable transactions include:
- Maxar Technologies acquired DigitalGlobe for approximately $2.4 billion in 2017, enhancing its satellite imaging capabilities and expanding its customer base across various sectors.
- Intelsat's merger with OneWeb, exploring potential synergies between GEO and LEO satellite services to strengthen market position and expand service offerings.
- SES pursuing strategic acquisitions and partnerships to bolster its position in the satellite communication market, focusing on enhancing capabilities in broadband connectivity and digital transformation.
Valuation Factors of the Sectors
Satellite Communication Sector
- EBITDA Multiples:
- General Market Range: EBITDA multiples in the satellite communication sector typically range from 8x to 12x. This range can vary significantly based on factors such as the company's market position, growth prospects, profitability, and the stability of its revenue streams.
- High-Growth Companies: Companies with strong growth trajectories, innovative technologies, or dominant market positions (like SpaceX’s Starlink) can command higher multiples, sometimes exceeding 15x.
- Mature Players: Established companies with stable cash flows and lower growth rates may see multiples in the lower end of the range, around 6x to 8x.
- Profit Multiples (P/E Ratios):
- General Market Range: Profit multiples (Price/Earnings ratios) in the satellite communication sector typically range from 20x to 35x.
- High-Growth Companies: Companies that are rapidly expanding their market share or launching new services may have higher P/E ratios, sometimes exceeding 40x.
- Mature Players: More mature companies with steady earnings and lower growth potential might have P/E ratios in the range of 15x to 20x.
Geospatial Sector
- EBITDA Multiples:
- General Market Range: EBITDA multiples in the geospatial sector usually range from 10x to 15x. This variation depends on the company's data assets, technological capabilities, and customer base.
- High-Growth Companies: Innovative companies with cutting-edge geospatial technologies, unique datasets, or strong partnerships often attract higher multiples, potentially 15x to 20x.
- Mature Players: Established geospatial firms with stable, recurring revenue streams may have EBITDA multiples in the range of 8x to 10x.
- Profit Multiples (P/E Ratios):
- General Market Range: Profit multiples in the geospatial sector generally range from 25x to 40x.
- High-Growth Companies: Companies with significant growth potential, particularly those involved in AI-driven geospatial analytics or new data collection technologies like drones, can see P/E ratios above 40x.
- Mature Players: Companies with steady earnings and lower growth potential may have P/E ratios in the range of 20x to 25x.
Factors Influencing Valuations
- Revenue Growth: Companies with higher revenue growth rates typically command higher EBITDA and profit multiples.
- Profit Margins: Higher profit margins can lead to higher valuation multiples, indicating efficient operations and strong market positioning.
- Market Position: Leading companies in their respective markets with strong competitive advantages often have higher multiples.
- Technology and Innovation: Firms with cutting-edge technologies or unique service offerings are valued higher due to their potential for future growth and market disruption.
- Recurring Revenue: Businesses with high levels of recurring revenue are generally valued higher due to the predictability and stability of their income streams.
- Regulatory Environment: Regulatory factors and government policies can impact valuations, particularly in heavily regulated industries like satellite communications.
Regulatory Environment
The regulatory environment plays a critical role in shaping satellite operations and market dynamics. Governments and international bodies regulate spectrum allocation, licensing requirements, and orbital debris mitigation practices to ensure safe and sustainable satellite operations. Companies like SES navigate these regulatory frameworks to provide a wide range of satellite communication services, including broadcasting, broadband connectivity, and government communications via their geostationary (GEO) and medium Earth orbit (MEO) satellites.

SpaceX Falcon 9 pierces California sky on June 17, 2024, delivering 20+ satellites to low earth orbit. (Source: Redmount)
Market Demand and Competition
Increasing demand for satellite-based services is a significant driver of innovation and investment in the sector. Competition among industry giants such as Iridium Communications and Telesat fuels advancements in satellite communication technologies. Iridium's LEO satellite constellation enables global voice and data communication services, catering to diverse industries and sectors that rely on reliable connectivity in remote and challenging environments. Telesat, meanwhile, is developing its Lightspeed constellation to deliver high-speed broadband connectivity globally, illustrating the competitive landscape in the race to provide next-generation satellite communication services.
Global Connectivity Initiatives
Initiatives aimed at expanding global connectivity underscore the transformative potential of satellite technology. Projects like SpaceX's Starlink and OneWeb's satellite constellations represent efforts to provide universal access to broadband internet, addressing global connectivity challenges and unlocking new economic opportunities worldwide. These initiatives highlight how private sector innovation can complement and extend the reach of traditional telecommunications infrastructure.
Geopolitical Considerations
Geopolitical dynamics also influence satellite operations, particularly in terms of spectrum access, satellite deployment permissions, and technology transfer restrictions. Companies must navigate these geopolitical considerations to foster international collaboration and expand their global footprint. Strategic partnerships and collaborations, such as those seen among industry leaders and government agencies, are essential for addressing regulatory complexities and advancing technological capabilities in a globally interconnected market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the satellite geospatial and communication sectors are at the forefront of technological innovation and global connectivity initiatives. Companies like SpaceX, Maxar Technologies, and SES are driving advancements in satellite technology while navigating regulatory challenges and geopolitical considerations. As market demand for reliable and high-performance satellite services continues to grow, these factors and forces will shape the future landscape of the satellite industry, offering new opportunities and challenges for stakeholders across the globe.
Redmount is a middle-market-oriented merchant bank with an advisory and investment platform built to serve the distinct needs of successful entrepreneurs, business leaders, and stewards of family wealth who value having a direct relationship with an experienced partner.
ABOUT REDMOUNT
Redmount is a merchant bank built since 1994 to meet the distinct needs of successful entrepreneurs, business owners, and smaller family offices that value a direct relationship with a trusted and experienced partner.
